NMN supplements typically show noticeable effects, such as increased energy and focus, within a few days to weeks, while long-term benefits like improved metabolism and anti-aging effects may take months.
What foods contain NMN naturally
- Nutrition
- October 17, 2024
- Alex L. partiQlar

Related Product
Is it possible to get enough NMN from natural food sources to increase NAD+ levels. To answer this question we will review different types of food with the highest amount of NMN: Edamame, Avocado and Broccoli.
Introduction
NMN is a precursor to Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide NAD+ a coenzyme that is involved in many metabolic processes, including DNA repair, gene expression, energy metabolism, and much more. In fact, it is so important that if somehow all NAD+ in our bodies ran out, we would not survive for more than a few seconds. The problem is that NAD+ levels drop with age. This is where NMN supplementation comes into play.
NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) is the immediate precursor of NAD+. The cell uses NMN to make NAD+. The reason we cannot take NAD directly is its big size which makes it hard to get into the cells. NMN is smaller and there is a specific transporter that brings it from the digestive system to blood circulation. When our body receives NMN, it transforms it into NAD+. Therefore, NMN has driven a tremendous amount of research and holds a huge promise for health benefits.
In this blog post, we aim to answer if it’s possible to get enough NMN from natural food sources to increase NAD+ levels. To do that – we will review different types of food with the highest amount of NMN as a natural source.
How much NMN do we need to boost NAD+?
There is no one right answer to this question, but let’s look at the research. In a recent study published in 2022 examining the efficacy of NMN, participants were divided into four groups, receiving a daily oral dose of either a placebo, 300 milligrams, 600 milligrams, or 900 milligrams of NMN over a period of 60 days.
The primary objective of the trial was to assess changes in NAD+ concentrations, with the secondary objective being to ensure the safety of the supplementation by examining clinical parameters at baseline and after 60 days. The study found that NMN supplementation increased NAD+ levels, with the benefits reaching the best point at 600 milligrams and no further improvements observed at 900 milligrams. All doses up to 900 milligrams were considered safe and well-tolerated.
Given the results of this study and the fact that most NMN supplements contain 500 milligrams per capsule (including partiQlar), in this article, we will compare the NMN amount from food sources with 500 mg of NMN as a daily dosage.
Foods that contain NMN naturally
While NMN supplements have gained popularity as effective NAD+ boosters, some people may prefer to obtain NMN from natural food sources. Some foods that contain NMN include vegetables, fruits, and animal products such as broccoli, avocado, beef, shrimp, etc. However, the question remains whether it is possible to consume enough NMN from food alone to boost NAD+ levels.
Let’s dive deeper into the foods which are known to have the highest amount of NMN in order to answer the question if it’s possible to get enough of this “magic molecule” from natural food sources. In this article amounts of NMN per different foods are based on a 2016 study published in “Cell Metabolism”. Let’s explore the top 3 natural sources of NMN foods – those with the highest NMN amount per 100g of product.
Edamame NMN
Edamame is a soybean also known as Japanese Soybean – is harvested at an early stage and is a tasty snack and appetizer. Edamame is a great source of plant-based protein and fiber, it is also one of the richest natural sources of NMN, with a concentration of approximately 0.47 – 1.88 mg per 100 grams.
To get 500mg of NMN from edamame, you would need to eat approximately 94 pounds (42,5 kg) of this soybean.
While it’s quite challenging to get enough NMN for your NAD+ boosting strategy, from this soybean, incorporating it into your diet can offer a range of health benefits and support overall wellness.
100 g of edamame contains (approximately):
- Vitamin C: 4.8 mg
- Vitamin K: 47 mcg
- Folate: 121 mcg
- Fiber: 5.2 g
- Potassium: 436 mg
- Calcium: 63 mg
- Iron: 1.8 mg NMN: 0.47 – 1.88 mg

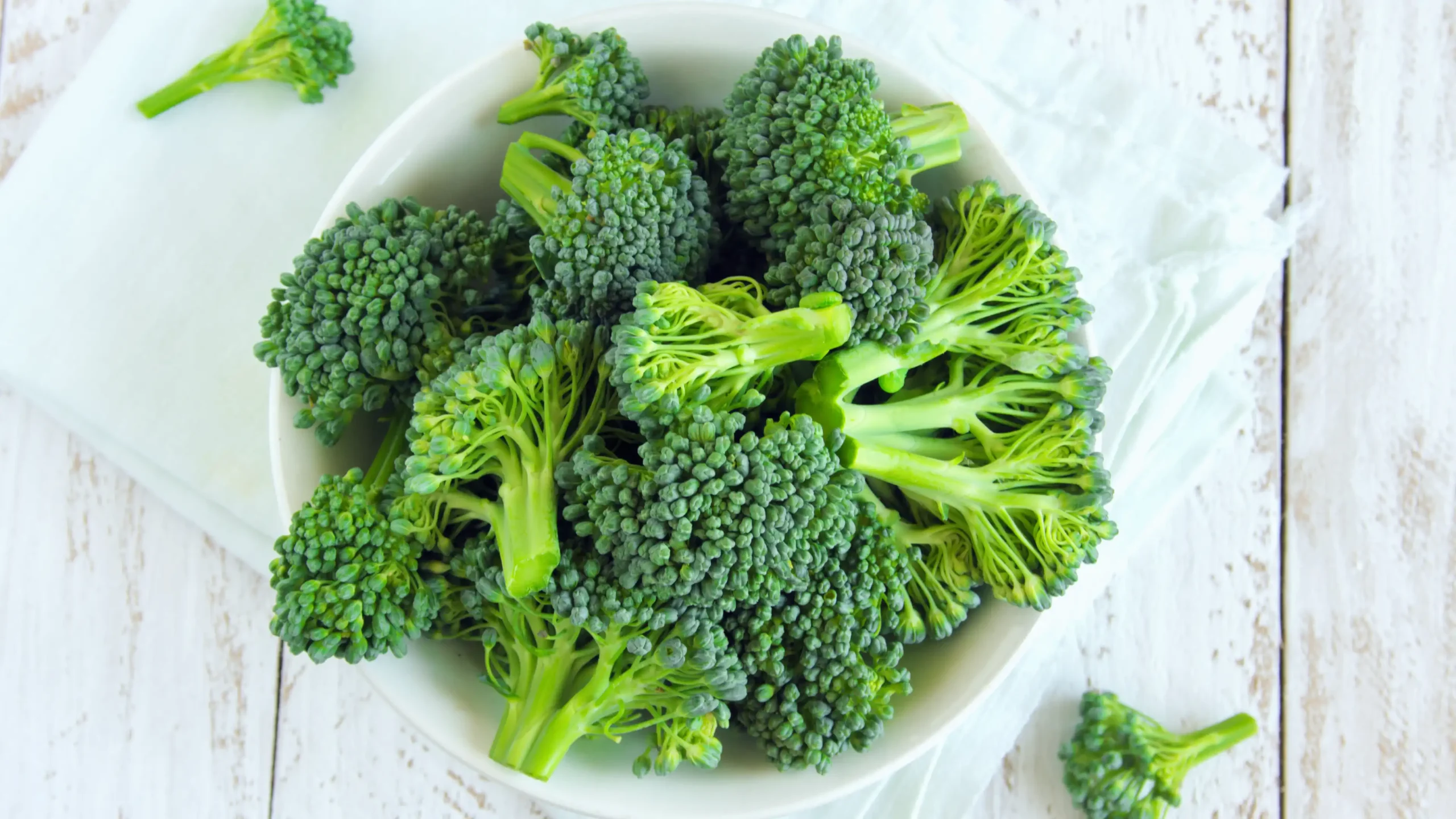
Broccoli NMN
Broccoli is a very well-known vegetable for its many health benefits and unique taste. One of the lesser-known benefits of broccoli is that it contains a small amount of NMN.
Broccoli contains approximately 0.25 – 1.12 mg (milligrams) of NMN per 100 grams. This means that to get 500 mg of NMN you would need to eat approximately 161 pounds (73 kg) of this vegetable in order to reach an effective NAD+ increase.
As per Edamame, it is also very challenging to achieve 500 mg of NMN from Broccoli, but it’s definitely recommended to include it in your diet as this vegetable is highly nutritious and contains a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds, so could be well incorporated in your longevity journey.
100 g. of Broccoli contains (approximately):
- Vitamin C: 89 mg
- Vitamin K: 101 mcg of vitamin K
- Folate 63 mcg of folate
- Fiber: 2.6 grams of fiber
- Potassium: 316 mg of potassium
- Calcium: 47 mg of calcium
- Iron: 0.7 mg of ironNMN: 0.25 – 1.12 mg
Avocado NMN
Avocados, have experienced a significant surge in demand in the United States during recent decades. In 1985, the amount of avocados consumed domestically was only 436 million pounds. However, this figure has multiplied by six, with over 2.7 billion pounds of the fruit being consumed by Americans in 2020. As per broccoli – probably most avocado lovers don’t know that in addition to its superfood benefits – it also contains NMN.
Avocado contains from 0.26 to 1.60mg NMN per 100g of product. To get 500mg of NMN from avocado, you would need to eat approximately 120 pounds (54 kg) of this superfood.
It is no surprise avocados are being called a superfood. These fruits are packed with nutrients such as fiber, potassium, Vitamin K, Vitamin C, Vitamin B6, and healthy fats. Healthy fats can support efforts to reduce cholesterol levels. Additionally, avocados contain antioxidants such as lutein and zeaxanthin, which support eye function and reduce the risk of age-related eye diseases. Avocado’s anti-inflammatory compounds, such as oleic acid, can also help reduce inflammation in the body and prevent chronic diseases. All concluded – must have food for your longevity goals.
100g of avocado contains (approximately):
- Vitamin C: 10 mg
- Vitamin K: 21 mcg
- Vitamin E: 2.07 mg
- Folate: 81 mcg
- Fiber: 6.7 grams
- Potassium: 485 mg
- Calcium: 12 mg
- Iron: 0.6 mg
- Carotenoids (Lutein and zeaxanthin): 185 mcg
- Oleic Acid: 9.8 g
- NMN: 0.26 to 1.60mg
Other foods that contain NMN naturally
According to the study published in Cell Metabolism Avocados, Broccoli, and Edamame are the top 3 foods with the highest concentration of NMN. There are other foods with less significant concentration per 100 g of product:
- Cucumber: 0.56 – 0.65 mg
- Cabbage: 0.0 – 0.9 mg
- Tomato: 0.26 – 0.30 mg
- Mushroom: 0.0 – 1.01 mg
- Raw Beef: 0.06 – 0.42 mg
It’s important to understand that simply consuming a diet that has some amount of NMN cannot guarantee an increase in NAD+ levels. But such a diet can certainly be beneficial to preserve your body’s natural stores of NAD+. If you’re looking to specifically increase your NAD levels, you may need to consider other options such as taking NMN supplements.

Final Thoughts
It is clear that even foods that contain the highest amounts of NMN naturally, such as edamame and broccoli, do not provide sufficient quantities of NMN for a meaningful boost in NAD+ levels. However, it is definitely still important to maintain a rich and varied diet that includes a range of nutrient-dense foods like all mentioned here and more.
If you are considering adding NMN to your diet through natural sources, it is worth noting that NMN is a relatively unstable compound that can break down at high temperatures. In fact, NMN is known to degrade rapidly above 95 degrees Fahrenheit, which means that cooking methods like boiling or roasting may significantly reduce the NMN content of foods.
Explore Products
Related Articles
Discover the connection between NMN and NAD, understand how they work regarding cellular energy production, and what makes them essential for optimal mitochondrial health.
This blog post discusses the FDA's recent decision to no longer classify NMN as a dietary supplement, examining the implications for its availability and safety in the market.

 Get an additional 15% off* with code: SUMMER
Get an additional 15% off* with code: SUMMER